Which Best Describes Lateral Inhibition in Sensory Processing
Central excitation of a retinal ganglion cell is surrounded by inhibition a classical example of spatial contrast enhancement a fundamental operation in processing spatial patterns in sensory systems. Increased blood flow to brain tissue in the visual or other sensory cortex b.
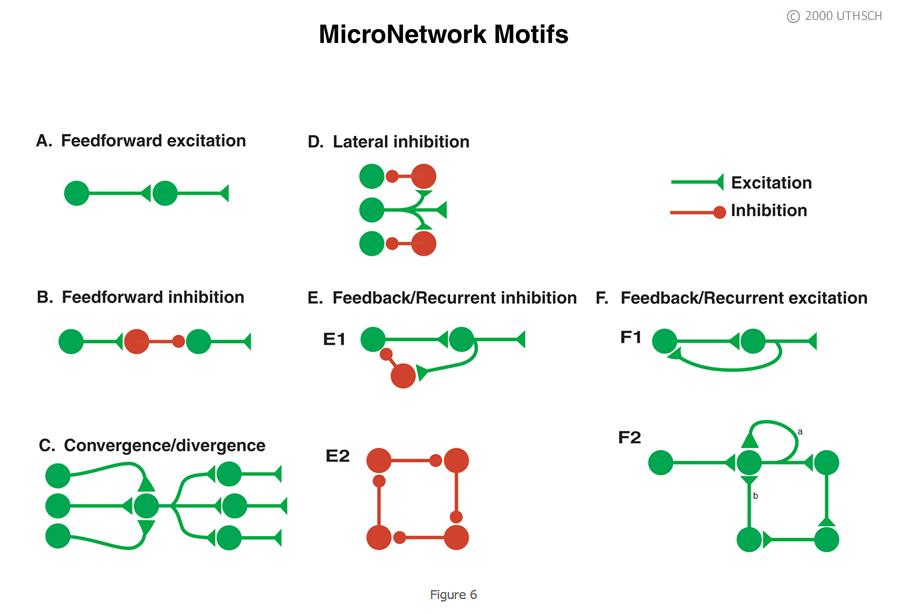
Introduction To Neurons And Neuronal Networks Section 1 Intro Chapter Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston
C Lateral inhibition occurs when communication is inhibited to second-order neurons receiving information from afferents associated with neighboring receptive fields.

. NPB 101 PRACTICE EXAM 1 Select the correct statements regarding sensory processing. The frequency of action potentials along pathways from the site of a stimulus is increased by lateral inhibition. Excessive sleep and relative inactivity.
D Lateral inhibition results in a stronger signal coming from second-order neurons associated with the central point of stimulation. Which best describes lateral inhibition in the somatic sensory system. It is also referred to as lateral antagonism and occurs primarily.
B Acuity is determined by the density of receptors the size of receptive fields and by. Lateral inhibition disables the spreading of action potentials from excited neurons to neighboring neurons in the lateral direction. One means of transformation involves interactions between.
Which best describes lateral inhibition in sensory processing. This prevents the spread of neuronal activity laterally. Presynaptic axoaxonal synapses reduce neurotransmitter release at excitatory synapses.
Lateral inhibition is a common theme in sensory physiology. Presynaptic axo-axonal synapses reduce neurotransmitter release at excitatory synapses. Inhibitory interneurons decrease action potentials from receptors at the periphery of a stimulated region.
A Most sensory systems are organized according to an anatomical scheme in which information from receptor cells is sent directly to cortex via a monosynaptic connection. In neurobiology lateral inhibition is the capacity of an excited neuron to reduce the activity of its neighbors. When a stimulus is maintained for a long time action potentials from sensory receptors decrease in.
Lateral inhibition is the phenomenon in which a neurons response to a stimulus is inhibited by the excitation of a neighboring neuron. When a stimulus is maintained for a long time action potentials from sensory receptors decrease in. Selective loss of GABA neurons in the various sensory areas of cortex c.
Lateral inhibition makes neurons more sensitive to spatially varying of stimulus than to spatially uniform stimulus. The frequency of action potentials along pathways from the site of a stimulus is increased by lateral inhibition. Which best describes lateral inhibition in sensory processing.
Lateral inhibition has been experimentally observed in the retina and the LGN of organisms 47. Which best describes lateral inhibition in the somatic sensory system. A Lateral inhibition in the retina.
Consequently there exists an increased contrast in excitation between neighbouring neurones allowing better sensory acuity. Which best describes lateral inhibition in sensory processing. Vasospasm leading to ischemia and disruption of neuronal activity in the relevant sensory areas of cortex e.
This creates a contrast in stimulation that allows increased sensory perception. Lateral inhibition is the ability of excited neurones to inhibit the activity of neighbouring neurones. This preview shows page 1 - 3 out of 27 pagespreview shows page 1 - 3 out of 27 pages.
Inhibitory neurons decrease action potentials from receptors at the periphery of a stimulated region Which region of the brain contains the primary visual cortex. Most sensory information destined for the neocortex is relayed through the thalamus where considerable transformation occurs 1 2. Lateral inhibition and the resultant sharpening of sensation occur within the central nervous system.
When a stimulus is maintained for a long time action potentials from sensory receptors decrease in. Which best describes lateral inhibition in sensory processing. Ratings 100 5 5 out of 5 people found this document helpful.
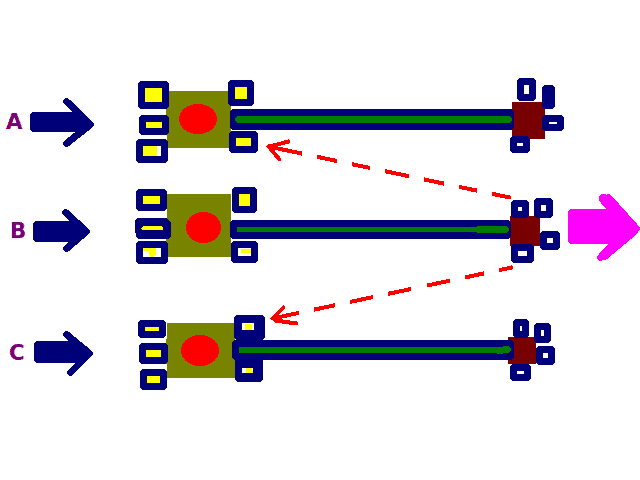
Those sensory neurons whose receptive fields are stimulated most strongly inhibitvia interneurons that pass laterally within the CNSsensory neurons that serve neighboring receptive fields.

Gevi Cell Type Specific Labelling And A Manifold Learning Approach Provide Evidence For Lateral Inhibition At The Population Level In The Mouse Hippocampal Ca1 Area Nakajima 2021 European Journal Of

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
30th Annual Computational Neuroscience Meeting Cns 2021 Meeting Abstracts Springerlink

Lateral Inhibition Sharpening Of Signal Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Studies Physiology
Sensory Coding And Contrast Invariance Emerge From The Control Of Plastic Inhibition Over Emergent Selectivity
Sensory Coding And Contrast Invariance Emerge From The Control Of Plastic Inhibition Over Emergent Selectivity

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Sensory Acuity Lateral Inhibition Two Point Discrimination Teachmephysiology

Cs 2015 Introduction To Neuronal Networks Christian Stricker Associate Professor For Systems Physiology Anums Jcsmr Anu Ppt Download

Introduction To Neurons And Neuronal Networks Section 1 Intro Chapter Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston

Inhibition Spike Threshold And Stimulus Selectivity In Primary Visual Cortex Neuron

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lateral Inhibition An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
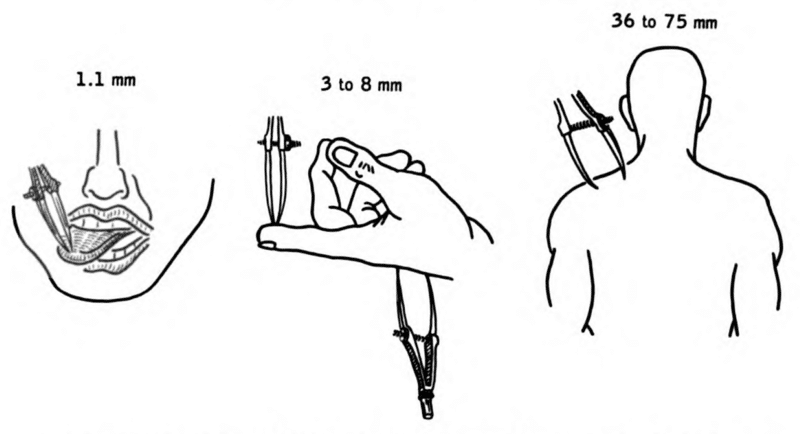
Sensory Acuity Lateral Inhibition Two Point Discrimination Teachmephysiology


Comments
Post a Comment